Note
This documentation is for the new OMERO 5.3 version. See the latest OMERO 5.2.x version or the previous versions page to find documentation for the OMERO version you are using if you have not upgraded yet.
OmeroContext¶
The entire OMERO application (on a single JVM) resides in a single ome.system.OmeroContext. Each call belongs additionally to a single org.hibernate.Session (which can span over multiple calls) and to a single ome.model.meta.Event (which is restricted to a single task).
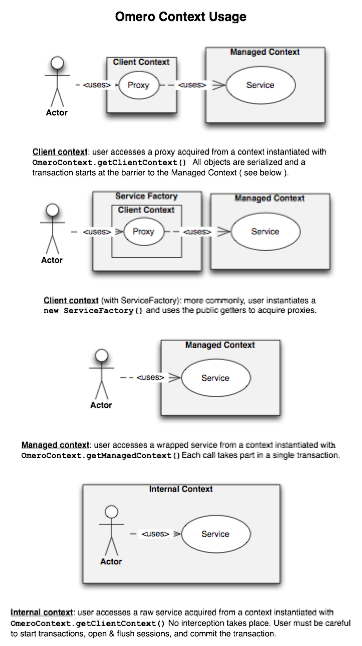
The container for all OMERO applications is the OmeroContext (components/common/src/ome/system/OmeroContext.java). Based on the Spring configuration backing the context, it can be one of client, internal, or managed. The use of a ServiceFactory simplifies this usage for the client.
Hibernate sessions¶
A Hibernate Session comprises a Unit-of-Work which translates for OMERO’s OME-Remote Objects model to a relational database. It keeps references to all Database-backed objects so that within a single session, object-identity stays constant and object changes can be persisted.
A session can span multiple calls by being disconnected from the underlying database transaction, and then reconnected to a new transaction on the next call (see components/server/src/ome/tools/hibernate/SessionHandler.java for the implementation).
For information about Events see OMERO events and provenance.